Dynamic Heterogeneous Attribute Analysis Technology for Complex Underground Engineering
2026-02-04In complex underground engineering, traditional geological models typically treat rock formations as homogeneous media, making it difficult to reveal micro-level variations in intrinsic properties such as water content, rock mass strength, gas content and stress distribution—these heterogeneities are the root causes of major hazards including water inrush, rock burst and gas outburst. Developed by Grid World, the dynamic heterogeneous attribute analysis technology breaks through the limitations of traditional modeling. By integrating massive geological and engineering data, it endows each unit in the 3D geological model with dynamically changing physicomechanical properties, realizing a fundamental leap fromvisualizing structural features toinsighting into intrinsic properties.
Core Analysis Dimensions: Accurate Characterization of Multiple Underground Hazards
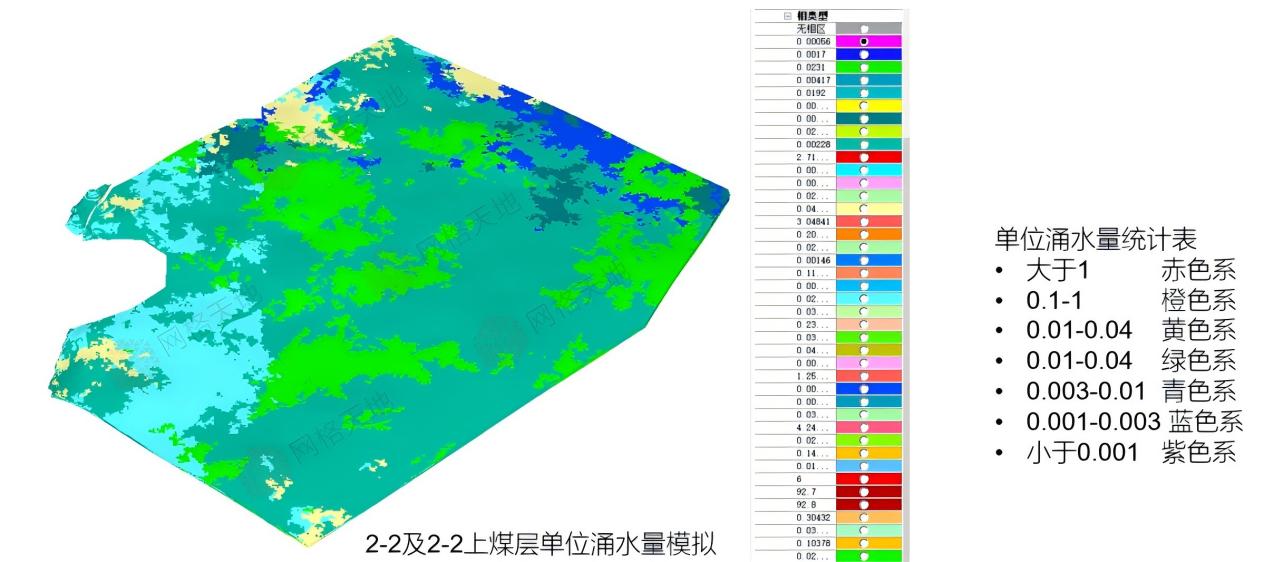
1. Specific Water Inflow Analysis: Quantifying Water Hazard Risks
By integrating formation permeability, water-bearing structure and other attributes, the system constructs a refined hydrogeological model to achieve the following goals:
· Precise delineation of risk zones: Predict the potential specific water inflow in different sections and strata, and visually mark high-risk areas for water inflow and inrush.
· Dynamic prediction of water inflow: Simulate the variation of underground water flow field in combination with excavation progress, predict the possible water inflow at the tunnel face, and provide key basis for the design of drainage systems.
· Optimization of dewatering schemes: Simulate the effects of different dewatering and drainage schemes, guide the formulation of cost-effective water control strategies, and transform passive drainage into active prevention and control.
2. Quantitative Lithological Analysis: Identifying Hidden Hazards
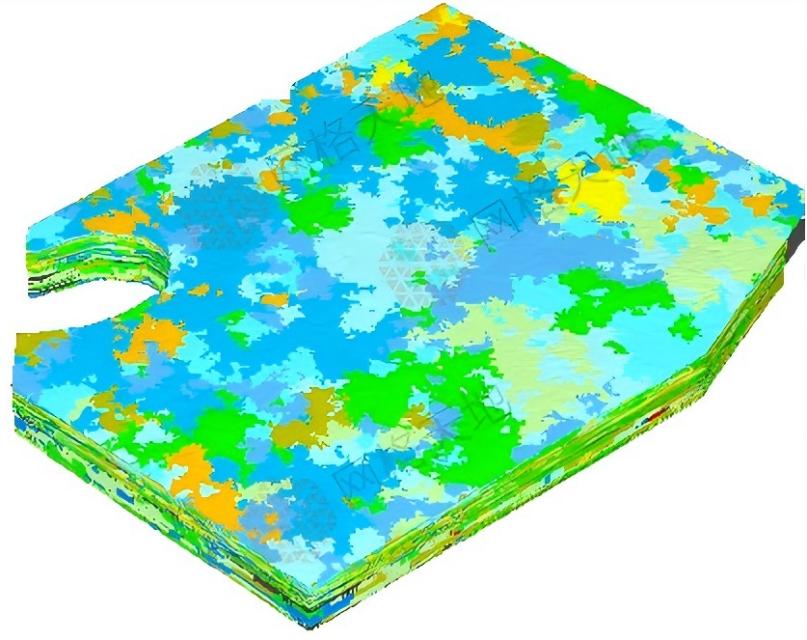
Going beyond traditional rock formation division, the technology conducts in-depth analysis of the spatial distribution of rock mass quality:
· Assignment of key parameters: Integrate quantitative parameters such as rock strength, integrity coefficient, weathering degree and alteration characteristics to truly reflect the spatial distribution of rock mass quality.
· Localization of weak interlayers: Precisely identify weak interlayers or fractured lenses with strength far lower than the surrounding rock in the model, which are common hidden hazards of tunnel collapse and slope instability.
· Differentiated support design: Recommend differentiated support types and parameters for rock mass areas with different attributes to balance safety and economic efficiency.
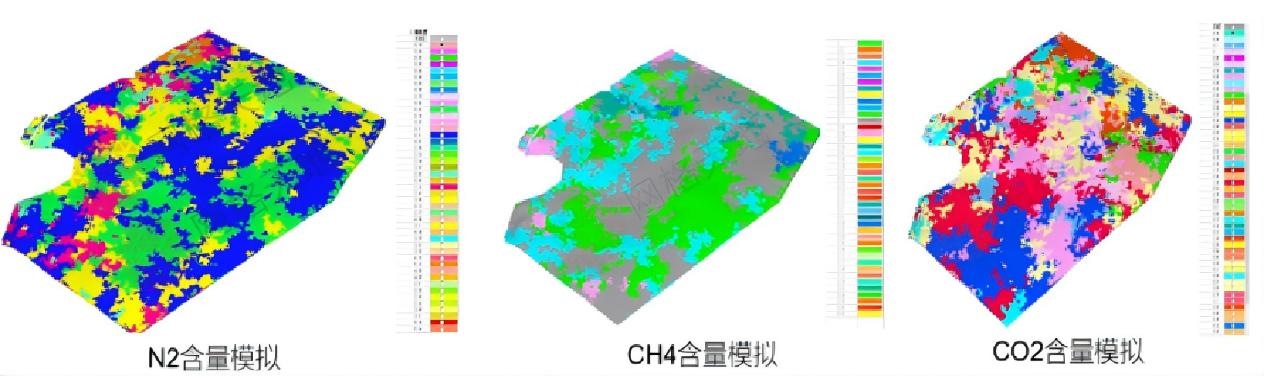
3. Intelligent Hazardous Gas Analysis: Safeguarding Operational Safety
Tailored for engineering environments such as coal mines and tunnels:
· Prediction of gas enrichment zones: Analyze the generation, migration and enrichment laws of hazardous gases based on geological structures, lithologic associations and coal seam horizons, and delineate high-risk zones.
· Dynamic simulation of gas concentration: Simulate gas migration and concentration distribution in roadway networks in combination with ventilation data, and issue early warnings of over-limit risks.
· Optimization of gas drainage and ventilation: Provide scientific guidance for the layout of gas drainage boreholes and the optimization of ventilation systems, fundamentally improving safety levels.
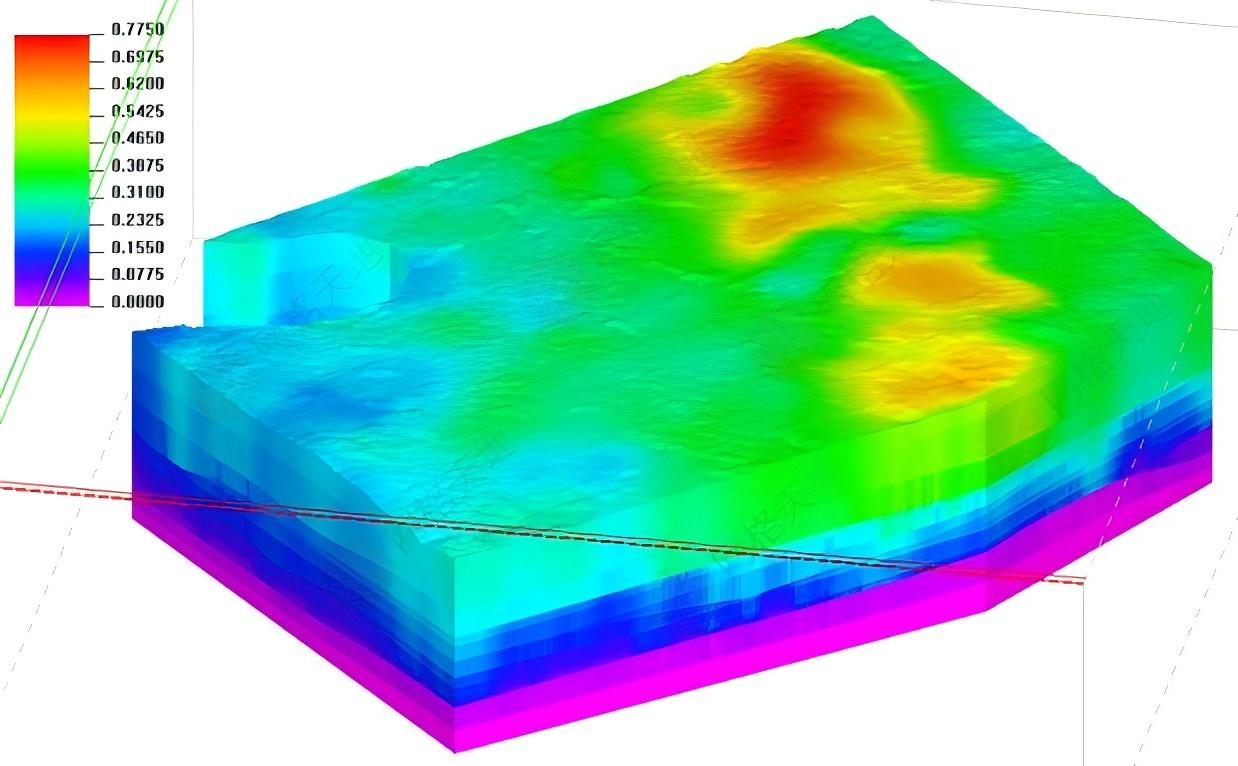
4. Dynamic Stress-Displacement Analysis: Foreseeing Rock Mass Behavior
Construct a realistic in-situ stress field model:
· Stress field visualization: Reveal the magnitude and directional distribution of the initial in-situ stress in the project area, and identify potential stress concentration areas and abnormal stress zones.
· Excavation disturbance simulation: Real-timely simulate the processes of surrounding rock stress redistribution, plastic zone development and displacement deformation with tunnel driving or excavation.
· Support efficiency evaluation: Evaluate the stress state of support structures such as bolts and linings in a realistic stress environment, issue early warnings of failure risks, and optimize the timing and strength of support.
Technical Value: From Experience-Based Judgment to Data-Driven Decision-Making
This technology is reshaping the risk management model of underground engineering across the entire project lifecycle:
· Design phase: Optimize project site selection and schemes based on attribute analysis to avoid inherent defects.
· Construction phase: Real-timely warn of abnormal attribute zones to achieve advanced quantitative prediction and dynamic regulation of risks.
· Operation phase: Continuously monitor attribute changes and assess the long-term stability of engineering structures.
Through heterogeneous attribute analysis, Grid World converts the hidden risks in underground space into clear, quantifiable and manageable decision-making parameters. We are working with industry partners to drive underground engineering into a new era ofdata-enabled stratigraphic insight and model-driven decision-making.





